Enterprises today begin to work aggressively to reach greater BPA (Business Process Automation) and offer cutting-edge customer experiences. They need to leverage multiple automation technologies to achieve these seamless customer experiences and automate the plethora of associated business processes. RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is one of the most significant automation technologies that play a vital role in the overall solutions.
RPA serves as the new technological salvation for companies by enhancing the business productivity and efficiency. Furthermore, when combined with the conventional business solutions, it can stimulate the digital transformation by enabling enterprises to control end-to-end business processes, which place the foundation for continuous process enhancement. As a business leader, what is the business value of RPA? Read on this blog to find the answer.
Innovations in RPA Services Today
Global use of RPA process has led to notable, positive effects on the business productivity. The RPA technology adoption has grown globally at a more rapid rate than ever before. It remains as the excellent business service front-runner across the industry. Sectors like insurance, banking, and financial services have started to experience the result of their uptake of RPA. Pleasantly, the range of sectors now investing in the RPA is enhanced, including utilities, manufacturing, hospitality, and mining to name a few. Let us highlight the applications of robotic process automation in various industries:
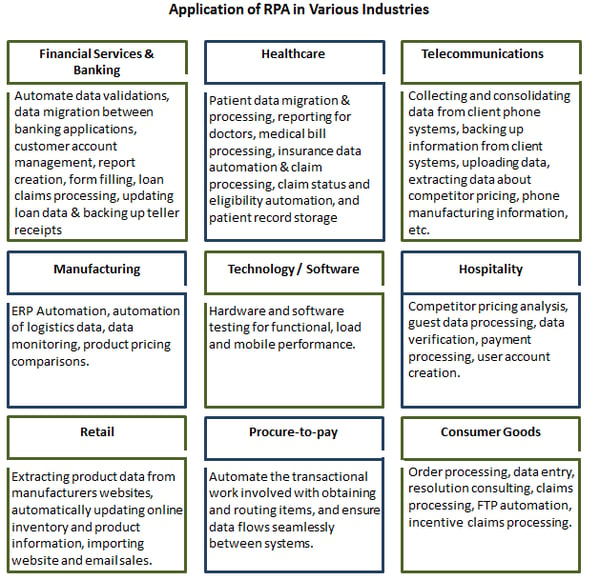
With its flexible and non-intrusive architecture, a robotic automation, which includes such a broad range of applications as well as business processes, has become a viable option. In addition, it also possesses the power to enable better management of the ever-changing labor market. Hence, the adoption of RPA transforms into a vital action that competitive businesses should take. According to a recent survey, 66% of respondents were thinking about the expansion of RPA programs and 70% were increased their funds for the RPA investment.
Factors that Increase Business ROI Out of RPA
Unquestionably, the adoption of RPA process is on the upswing due to its capability to deliver rapid ROI and increased control over operations. However, it is not good to measure the ROI of RPA technologies with just financial gains alone – especially if those are due to labor savings. Because this approach doesn’t justify the whole capability of the RPA automation as there are several business benefits. The followings are some influences of RPA services on the businesses that boost the ROI:
Key Characteristics of Robots Build With RPA Software
The RPA robots include the following key characteristics:
- User-Interface Interaction - The RPA bots can mimic human interaction on the UI of an IT system like entering information into fields; make cursor jumps, push buttons, etc. The script of the robot includes conditions and rules to pretend actual user behavior. Businesses can develop the scripts with robot developers or record directly on the system with RPA technology.
- Process Execution - The RPA robot can run processes as like how human executes them including user interface interaction.
- High Volume Data Handling – The RPA bots can handle high volumes of data in the user interface and process interaction. They transport and use the data from external storage or resulting from a user interface.
- Learning Capability – Advanced RPA robots can integrate with AI by employing machine learning algorithms. Machine learning permits the robots to automatically absorb and enhance from experience. Therefore, the robot developers don’t need to do any scripts.
Benefits of RPA (Robotic Process Automation) in Business Perspective
Each industry should aware where RPA is applicable and what values it can offer to their business in view of the evolution of the operating model as well as IT landscape. Here are the eight most significant of those benefits:
1. Increase Productivity
Most of the robots made from the RPA system are fully focused on specific tasks. Just consider an RPA bot that permits a worker to create a monthly report in 20 minutes, which manually endures four hours. The robots can calculate, click and navigate through the screen in a few seconds. This time saving is not adequate to replace the worker with the robot. However, it does make that worker more productive and that, in turn, will support future cost avoidance. With process automation, the business will enjoy a boost in its productivity.
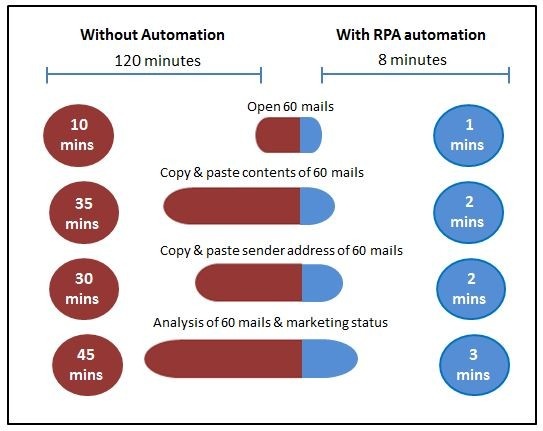
2. Increase Efficiency
RPA software never needs a break – it can work 24 hours a day, 7 days a week and 365 days a year. Similarly, it does not take a vacation or fall in sick. Generally, a single RPA robot can be equal to the two to five full-time employees, and even more. Robots can complete same volume of work in less time or more volume of work at the same time. Just consider this example for the RPA efficiency:
3. Enhance Accuracy
Since employees are human, there is a chance for mistakes. The main feature of robotic process automation is its power to eliminate processing errors. As it is not a turn-key solution, it requires testing, training as well as governance. However, as long as the business processes are properly optimized and accurately mapped, businesses need not be concerned that the robots will make errors that their employees might.
4. Increase Security
Among the benefits of robotic process automation, the most convincing one is that it functions on a granular level. As the bot performs only the single tasks, there is no worry of information leakage from one part to another. Here, the data accesses are well controlled and documented. The most ignored factor in RPA implementation is the myth that robots may replace the need for human employees. However, RPA implementation demands the employees who handle the system with the skills to control a workforce that includes both people and machines.
5. Boost Scalability Opportunities
Robotic process automation offers flexibility to adapt what the moment demands in means of the type and the number of tasks needed for any given objective. Robotic automation can support businesses to accommodate the selected requirements of certain objectives. Since the robotic workforce is adjustable to time- and task- specific requirements, even smaller businesses can manage the unpredictably evolving market demands.
6. Improve Analytics
RPA technologies allow organizations to gather data about task execution that can be employed for analytical purposes. Work volume patterns, cycle times, errors and exceptions are few of them. Perceptions attained from such analysis can benefit in several ways like supporting process improvement initiatives. When data is efficiently gathered, compared and differentiated to data gathered in other fields, it permits for better decision making on the micro as well as macro levels. In addition, the company can determine gaps where the business processes could be further streamlined to enhance efficiency.
7. Enhance Customer Service
Most of the companies today can have a hard time to meet the highly varied customer demands. However, in an RPA adopted company, where the routine, repetitive and dull tasks are handed over to the robots, so the employees can better concentrate on customer care. With the skilled and proficient workers, the companies can address the customer needs. Moreover, they can understand the requirements of the customer with automatically generated reports like those results from analytics.
8. Non-disruptive
Some organizations are uncertain to replace legacy systems due to the cost or the business downtime and complexity related to the challenge of IT infrastructures. In case a significant IT promotion is not guaranteed, the RPA system can be utilized to lengthen the lifetime of the legacy system and automate daily operations. The RPA tools communicate with systems at the presentation layer or UI end as like how humans do. Robots can even use their own user IDs and passwords. In such a manner, implementing robotic process automation in a business is not complex or disruptive approach since the core technology program remains intact.
RPA has the power to streamline your business processes and reduce operational costs. Want to know how this could impact your bottom line? Use our ROI Calculator to calculate the potential financial benefits of implementing RPA in your business
Conclusion:
It is significant for an organization to adopt RPA solutions to have a better insight into what their primary business goals are. If the available business processes and IT infrastructure are effective, then the business can consider RPA automation as a user-friendly tool to meet their automation objectives. Even if the process, platforms, and applications are outdated, then the RPA can be used to solve the issues. Overall, at this age of the digital transformation, robotic process automation is highly required for companies to nurture the healthy working environment.






